The structure and size of oxygen lance pipes are two critical factors that we need to understand when we want to avoid unnecessary expenses during the operation. The structure determines the quality and functionality of the pipe, while the size dictates its suitability for specific applications. In this blog post, we will explore these crucial aspects and how they impact the selection and utilization of Daiwa Thermic Lance in the actual circumstances.
Structure of Daiwa Thermic Lance
Daiwa Thermic Lance is basically used for cutting, boring or demolishing large-sized materials such as iron castings, stainless steels, brass, non-ferrous metals, refractory materials, concrete, ceramic, natural stone, etc.
To fit in with this that cutting purpose, its structure has been tailored into two variants: Type T and Type W. Below, you'll find the descriptions for the structure of each type.
Structure of Daiwa Thermic Lance (Type T)
Daiwa Thermic Lance with Type T consists of three layers, which are essential for properly regulating the oxygen flow rate during cutting operations.
1. An outer pipe
The outer cylindrical structure of Daiwa Thermic Lance is often made of mild steel. It serves as a protective sheath for the inner core components and contains the reactants necessary for the exothermic cutting. The outer pipe is usually available in various lengths and diameters to suit different cutting requirements.
2. A mixture of iron wires
The inner core of Daiwa Thermic Lance is where the exothermic cutting takes place. It typically consists of a mixture of metal alloy rods, such as iron. These rods are compactly arranged within the lance pipe and play a central role in generating the extreme heat required for cutting.
3. An inner pipe
The inner pipe of Daiwa Thermic Lance is deliberately positioned at the center of the hole in order to maintain a balance with the surrounding iron wires. This unique arrangement ensures optimum performance and efficiency during operation, allowing for precise and controlled thermal cutting and piercing processes.
.png?width=600&height=600&name=Structure%20of%20Daiwa%20Thermic%20Lance%20(Type%20T).png)
From an engineer's perspective, it can be observed that the oxygen flow rate passing through Type T will be lower, the pressure will be less, and it will cut softer materials compared to Type W.
Structure of Daiwa Thermic Lance (Type W)
The structure of Daiwa Thermic Lance with Type W is quite similar to Type T, but it does not have an inner pipe at the center of the lance pipe.
1. An outer pipe
Following the pattern of Type T, Type W also has a cylindrical structure surrounding the iron wires inserted inside Daiwa Thermic Lance. With this protective shield, factory operators can rest assured knowing that the iron wires inside Daiwa Thermic Lance will remain secure and tightly in place throughout the whole operation.
2. A mixture of iron wires
For Type W, Daiwa Thermic Lance contains a greater number of iron wires compared to Type T. This is because the absence of a hollow inner pipe at the center of the lance pipe allows for more space to insert the iron wires. As a result, Type W exhibits stronger oxygen flow rate, pressure, and cutting force, making it the ideal choice for cutting through harder materials such as concrete. Additionally, the heat dissipation and spread around Type W are superior, giving it an advantage over Type T.
.png?width=600&height=600&name=Structure%20of%20Daiwa%20Thermic%20Lance%20(Type%20W).png)
RELATED POST
Size of Daiwa Thermic Lance
Daiwa Thermic Lance comes in various sizes, and the choice of size significantly impacts its suitability for specific applications. The size of the lance is determined by factors like its diameter, thickness and length, and these characteristics play a crucial role in determining its effectiveness for different tasks.
The choice of lance size depends on the specific application. For example:
- Large Diameter, Long Lances: These are ideal for industrial demolition or cutting through large steel beams and structures.
- Smaller Diameter, Short Lances: These are used for precision cutting in situations where fine control is needed, like in the construction of sculptures or artistic metalwork.
- Medium-sized Lances: These are versatile and can handle a range of general cutting tasks, making them suitable for many applications.
Below is the standard size of Daiwa Thermic Lance in both Type T and Type W.
Size of Daiwa Thermic Lance (Type T)
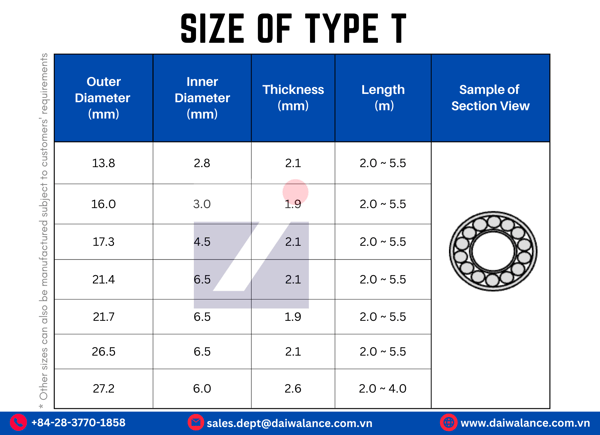
Size of Daiwa Thermic Lance (Type W)
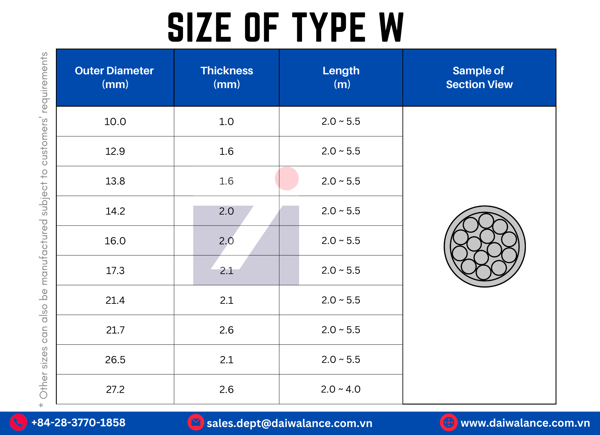
Conclusion
In conclusion, to ensure a proper bulk purchase, it is important to know exactly what you want. Not only the quality of the products, but also the structure, size, and other factors such as maintenance needs, should be taken into consideration.
Clearly communicate the desired application to the manufacturer.
Think about if there are any specific notes or instructions that require attention when using the products. Request a sample for evaluation in advance.
Do all the things that you can.
But alternatively, a simpler approach would be to enlist the help of an expert who can handle the entire process from start to finish. Feel free to contact us for assistance if you want to become more confident in your decision.
- Category:
- Daiwa Lance Products
- Keyword:
- introduction to thermic lance




















