Diffusion
Diffusion technology refers to a process in which atoms, molecules, or particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, typically through a medium or material. This movement occurs due to random thermal motion and is driven by the natural tendency of particles to spread out and achieve a state of equilibrium.
In various industries and scientific fields, diffusion technology is employed for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Materials Science
- Chemical Engineering
- Biology
- Pharmaceuticals
- Environmental Science
- Metallurgy
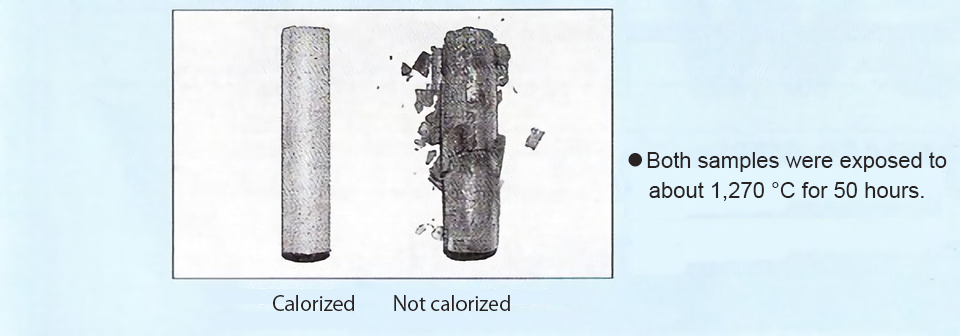
As mentioned earlier, diffusion technology is used to create materials like calorized lance pipes. It involves the infusion of one material (e.g., aluminum) into another (e.g., steel) to enhance certain properties.
The rate of diffusion depends on factors such as temperature, concentration gradient, and the nature of the materials involved. Diffusion can occur in gases, liquids, and solids, although the mechanisms and rates may differ in each phase. It's a fundamental concept in both scientific research and various industrial applications.














