Decarbonization is transforming the global economy in a positive way to the environment. If previously, most of the steel production primarily comes from BF, now steelmakers can have another option to use EAF - a more environmentally friendly type of metallurgical furnace which consumes steel scraps as raw materials to produce steel rather than natural resources like iron ores.
Continuing the last topic about the general image of how Thermic Lance - a high temperature burner oxygen lance pipe - is used in Blast Furnace, this time, we shift our focus on a different scenario: Thermic Lance in EAF.
In this article, you will have a chance to reflect on how EAF works to maximize operational systems as well as know which specific type of Thermic Lance is commonly applied for each circumstance.
How EAF Operates
EAF, abbreviated for Electric Arc Furnace, is a product of the industrial revolution in an effort to reduce carbon dioxide emission accumulating in the steel manufacturing process.
Structured with graphite electrodes attached directly to a molten bath in a vertical position, EAF uses electrical power to generate heat and melt steel scrap into slag.
Compared to BF, EAF is more efficient in a way that it helps:
- Replace raw materials with 100% steel scraps instead of natural resources
- Take up less space with smaller size
- Produce steels with shorter time
- Lower price for the initial investment
- Reduce CO2 better by not requiring a substantial amount of coke
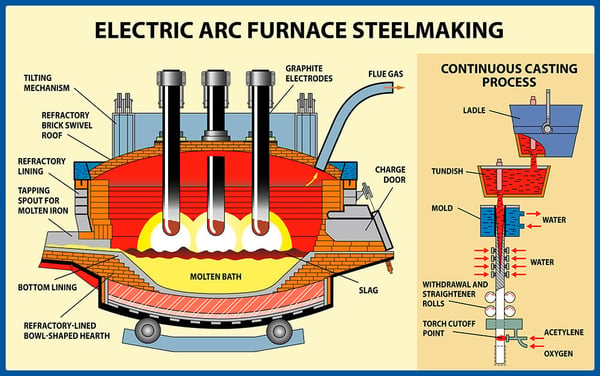
(A Brief Description of Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking)
The advantage of EAF is great, but if we know how to run the entire manufacturing process smoothly from A to Z, it'll be even better. Let's see how we could use Thermic Lance to enhance the efficiency of the steelmaking process of EAF in the next section.
RELATED POST
Thermic Lance Sharp Cut against Large Steel Scrap
To decrease carbon footprint, EAF-based production uses scraps as the main materials.
But this, on the other hand, brings out a critical issue for the steelmakers concerning large steel scrap pre-treatment.
It is because of the fact that originally not all steel scraps in the scrapyard have the same size.
Steel scraps may be smaller or bigger than the typical EAF size, causing significant difficulties in transporting them into EAF.
In this case, using a Thermic Lance of Type-T with a popular outside diameter ø17.3 mm x 3,000 mm to cut massively thick steel scraps into smaller pieces can help curtail the time necessary for transporting and melting process.
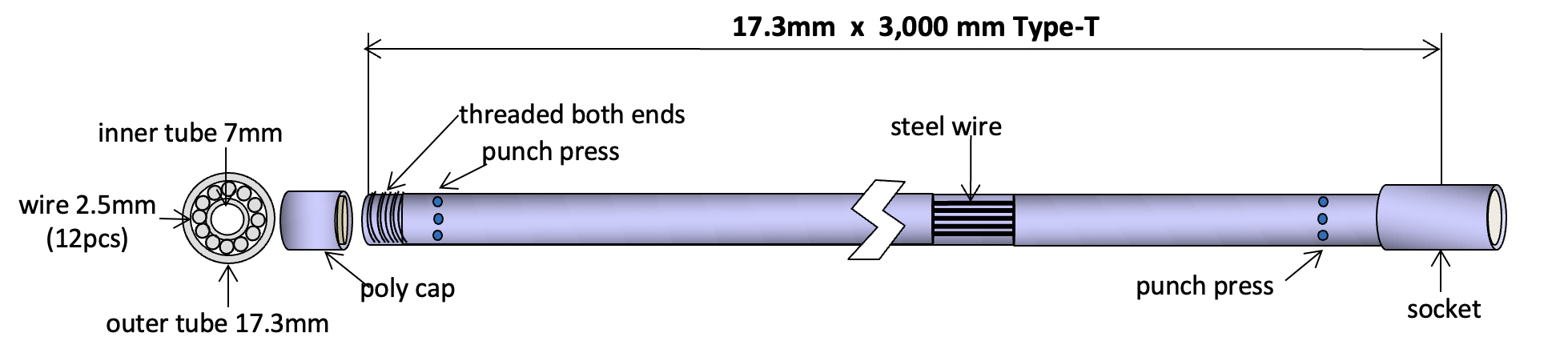
(A schematic diagram of a Type-T Thermic Lance with commonly used dimension)
Speedy Slag Removal with Thermal Energy
Similar to BF, molten slag after solidification during EAF-based production will be getting unbearable to deal with over the time.
The location that molten slag adheres to can be anywhere: in the ladle cars, tundish nozzles, or continuous casting equipment, particularly irritating to continue the steelmaking process without removing it.
If you're attempting to remove slag expecting a speedy performance on the surface of mechanical equipment, you can use a Thermic Lance of Type-W with an outside diameter of ø17.3 mm x 3,000 mm.
Inserted by 19pcs of 2.5 mm small steel wires inside, Thermic Lance Type-W effectively harnesses oxygen to produce a super hot temperature up to 4,000°C higher the melting point of slag at 1,780°C and make slag quickly splash away.
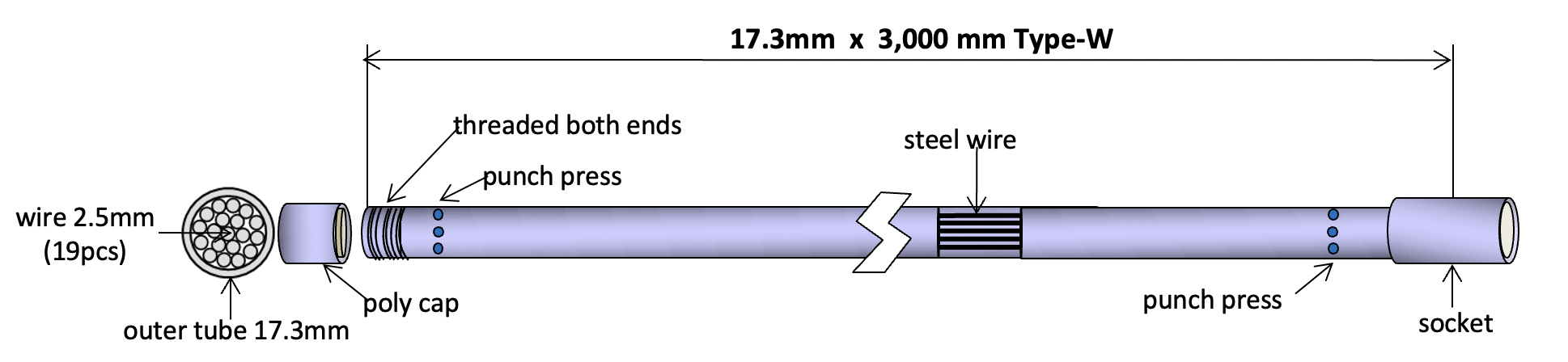
(A schematic diagram of a Type-W Thermic Lance with commonly used dimension)
Here's a tip for you. Thermic Lance will burn up a lot like a little sparkler during the combustion, so don’t forget to wear a full set of protective clothing while keeping a safe distance like the picture below.

(A full set of protective clothing at the factory)
Floor Cleanup with Thermic Lance Custom Sizes
Mobility and portability are two important features of Thermic Lance.
Mobility in a way that we can bring Thermic Lance freely and easily anywhere in the steel mill because its length is often only 3,000 mm.
Portability in a way that we will have little concern to carry Thermic Lance since its weight is only a few kilograms.
With these two features, a Type-W Thermic Lance would be potentially useful for sweeping away molten slag sticking to the steel mill floor every time EAF production is finished.
Particularly, in the situation when slag is too small to clean up, rather than the nominal dimension of outside diameter around ø17.3 mm x 3,000 mm, we can freely choose a smaller size of Thermic Lance around ø12.7 mm x 2,750 mm or even a bigger size of ø27.2 mm x 3,000 mm.
If you wish to see other sizes of Thermic Lance that our company can offer, download the catalogue below for more information. Or just in case you have any special requests on the tailor-made size of it, don't hesitate to contact us by clicking on this link.
Conclusion
Now that you know how EAF works to reduce the carbon dioxide emission and in which way Thermic Lance with different types could support the engineers to optimize the steelmaking process with heavy steel scrap pre-treatment and slag removal.
However, the good properties of products are not all the things that you should keep in mind when buying an oxygen lance pipe for your factory.
In addition to the main functions, the best ways to manipulate the equipment or specialist advice on suitable size also play a crucial role in helping you to find the right fit for each manufacturing process.
Upgrading yourself with fascinating steel insights is another good way to make your factory more efficient. Just hit the button here to subscribe to our blog and receive the updated news! It's free and informative!
- Category:
- Daiwa Lance Products
- Keyword:
- introduction to thermic lance





















