Taphole
Taphole (also known as iron notch) is a hole situated above the hearth of a furnace or ladle and generally used for tapping slag or molten metal during metallurgical processes. It can be found in Electric Arc Furnace, Blast Furnace or some smelters such as Copper Smelter, Silicon Smelters, Lead Smelters, Nonferrous Smelters, etc.
Being a critical component in improving performance and longevity of the furnace, taphole is carefully examined and redesigned over the years.
In the metal making process, after metals are melted into a liquid and slags are formed, an oxygen lance pipe covered with heat-resistant materials will often be used in order to open a taphole from a safe enough distance.
The following diagram illustrates example tapholes in two of the most common steel making furnaces.
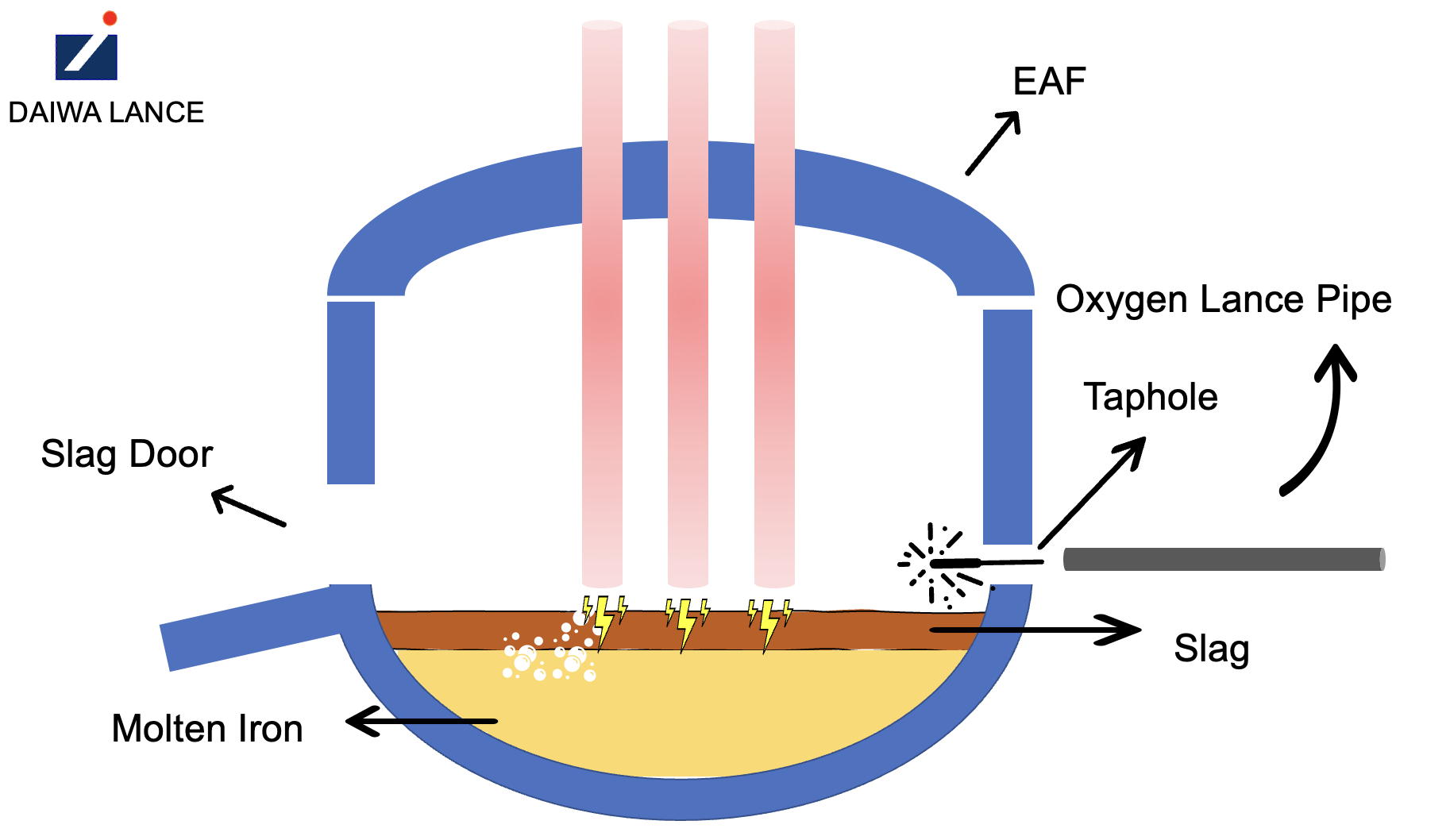
An illustration diagram of the taphole and oxygen lance pipe in Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
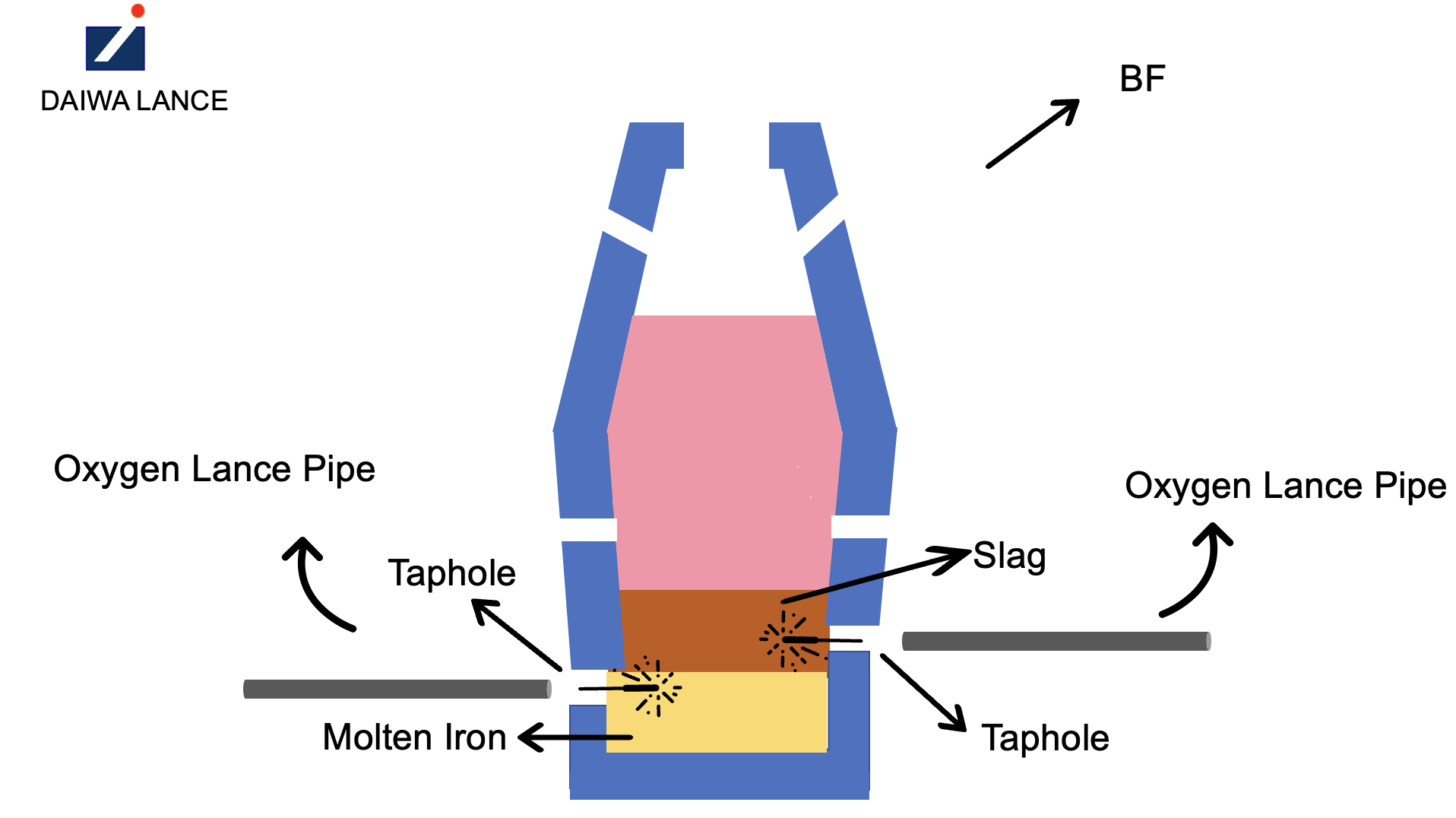
An illustration diagram of the taphole and oxygen lance pipe in
Blast Furnace (BF)














